Hazardous materials – Act now! and keep people safe.

Unlike other hazardous materials regulations, fire and building codes specify a building’s design and construction to prevent and mitigate fires and emergencies involving hazardous materials. The occupancy classification establishes fire and life safety features needed to protect building occupants, firefighters, and emergency responders, so it’s essential to get it right.
There are six concepts every code official should master to verify the occupancy classification of buildings containing hazardous materials successfully.
The process
The process to determine whether a high-hazard (Group H) occupancy is needed is the same whether you are evaluating hazardous materials in wholesale/retail sales occupancies, higher education laboratory suites, or any other occupancy. What differs between these scenarios is the number of control areas and quantities of hazardous materials allowed before a Group H classification applies.
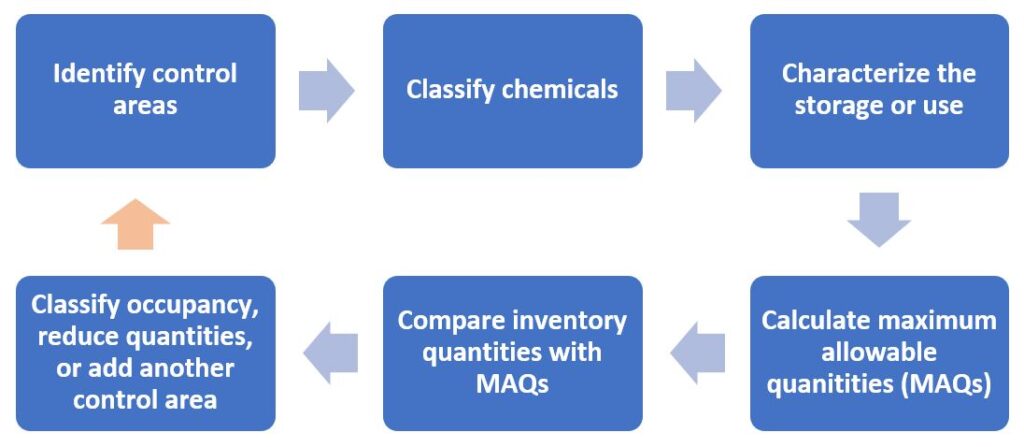
Process steps:
- identify the control area(s)
- classify the hazardous materials in the control area
- characterize and determine the hazmat quantities in each condition (i.e., storage, closed-use and open-use)
- calculate the maximum allowable quantities (MAQs) for relevant hazard classes
- evaluate whether inventory quantities exceed the MAQs
- decide whether to classify the occupancy, reduce quantities or create additional control areas.